July 3, 2024
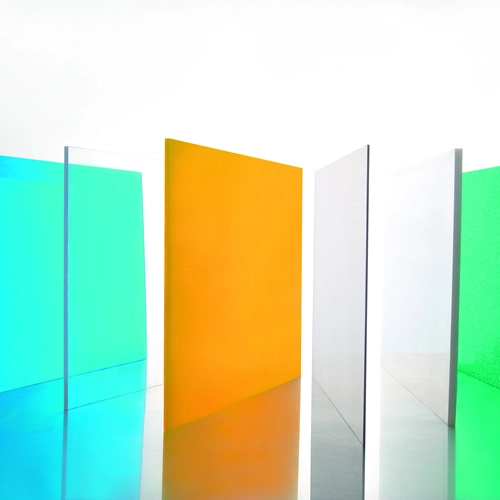
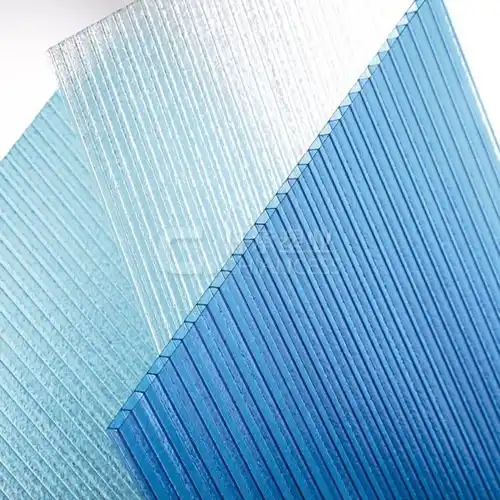
Polycarbonate is a flexible and strong thermoplastic polymer known for its solidarity, influence opposition, and straightforwardness. Automotive, construction, electronics, and medical devices are just a few of the many sectors in which it finds widespread application. One of polycarbonate's most important properties is its ability to be colored. This causes it to seem more appealing and makes it work better in various applications.
In this article, I will talk about the benefits of Colored polycarbonate solid sheet, the challenges of the process, and the methods and techniques used to add color to it.
Methods of Coloring Polycarbonate
Masterbatch Coloring
Masterbatch coloring is one of the most common methods used to add color to polycarbonate. A masterbatch is a concentrated mixture of pigments or dyes encapsulated in a carrier resin. This masterbatch is then added to the polycarbonate during the manufacturing process. The key benefits of using masterbatch coloring include:
- Consistency: Ensures uniform color distribution throughout the material.
- Customization: Allows for the creation of custom colors and shades.
- Efficiency: Simplifies the coloring process by integrating it with the production line.
The masterbatch is typically added to the polycarbonate resin in a specific ratio, ensuring the desired color intensity and consistency. This method is particularly popular in the automotive and electronics industries, where precise color matching is crucial.
Liquid Coloring
Liquid coloring involves the use of liquid dyes or pigments that are mixed with the polycarbonate resin. This method offers several advantages, including:
- Flexibility: Easier to achieve a wide range of colors and shades.
- Cost-Effective: Often more economical than masterbatch coloring for small production runs.
- Improved Dispersion: Liquid colors tend to disperse more evenly within the polymer matrix.
However, liquid coloring requires specialized equipment and careful handling to prevent contamination and ensure consistent color quality. This method is commonly used in the production of consumer goods, such as eyewear and household appliances.
Dry Blending
Dry blending, also known as dry powder coloring, involves mixing powdered pigments with Colored polycarbonate solid sheet resin before processing. This method is suitable for applications where high color intensity is required. Key benefits of dry blending include:
- High Color Intensity: Allows for the creation of vibrant and deep colors.
- Cost Savings: Eliminates the need for liquid carriers or masterbatch carriers.
However, dry blending can be challenging due to the potential for uneven color distribution and dust generation. Proper mixing techniques and equipment are essential to achieve consistent results.
Co-Extrusion
Co-extrusion is a technique where a colored layer of polycarbonate is extruded simultaneously with a clear or differently colored layer. This method is used to create multi-layered products with distinct color effects. Co-extrusion offers several benefits:
- Layered Effects: Allows for the creation of products with different colors on the surface and core.
- Durability: Enhances the material's resistance to UV radiation and weathering.
Co-extrusion is commonly used in the production of sheets and films for applications such as signage, roofing, and protective glazing.
Challenges in Coloring Polycarbonate
Color Stability
One of the main challenges in Colored polycarbonate solid sheet is maintaining color stability under various environmental conditions. To address this issue, UV stabilizers and antioxidants are often added to the polycarbonate resin to enhance its color stability and longevity.
Compatibility of Pigments and Dyes
Polycarbonate is not compatible with all dyes and pigments. Certain colorants can influence the material's mechanical properties or cause handling issues. As a result, it's critical to choose colorants designed specifically for polycarbonate. To ensure optimal performance, compatibility testing and quality control measures are necessary.
Processing Conditions
The processing conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and shear rate, can significantly impact the final color of the polycarbonate product. Variations in these parameters can lead to color inconsistencies and defects. Manufacturers must carefully control and monitor the processing conditions to achieve consistent and high-quality coloration.
Applications of Colored Polycarbonate
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, Colored polycarbonate solid sheet is frequently used for interior trims, dashboard panels, and exterior lighting. The vehicle's aesthetic appeal and brand identity are enhanced by matching the color of these parts to the overall design.
Electronics and Consumer Goods
In the hardware and buyer merchandise areas, hued polycarbonate is utilized for the lodgings of gadgets, for example, cell phones, PCs, and home devices. The vibrant and customizable colors of polycarbonate contribute to the visual appeal and marketability of these products. Moreover, the material's transparency and optical clarity make it ideal for applications that require light transmission, such as LED covers and lenses.
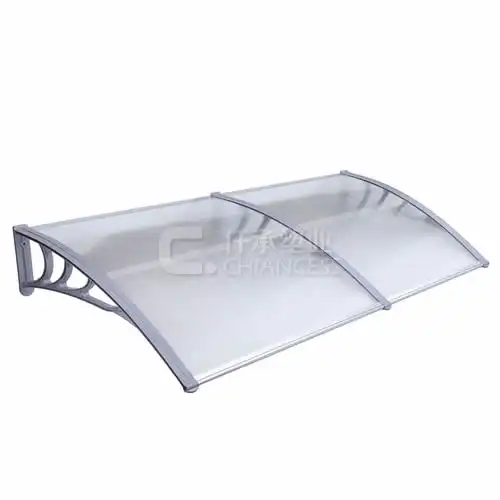
Construction and Architecture
In architecture and construction, colored polycarbonate is used for roofing, glazing, and decorative panels. The material's capacity to communicate light while giving UV security makes it appropriate for lookout windows, nurseries, and façade cladding. Due to their durability and resistance to the elements, colored polycarbonate sheets are also utilized in signage and advertising displays.
Benefits of Coloring Polycarbonate
Aesthetic Appeal
One of the primary benefits of coloring polycarbonate is the enhanced aesthetic appeal. Colored polycarbonate products can be tailored to match specific design requirements and branding guidelines. The availability of a wide range of colors and finishes allows for creative and visually striking designs.
Functional Enhancements
Coloring polycarbonate can also provide functional enhancements, such as improved UV resistance and thermal stability. Coverings and vehicle windows, for instance, can profit from hazier tints since they can retain more intensity and decrease glare. Additionally, certain pigments can provide anti-static or flame-retardant properties, expanding the material's versatility.
Increased Marketability
Colored polycarbonate products are often more attractive to consumers, increasing their marketability and competitiveness. The ability to offer custom colors and finishes can differentiate products from competitors and appeal to specific customer preferences. In the automotive and buyer hardware industries, style and configuration play a significant role in purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
Colored polycarbonate solid sheet is a multifaceted process that involves various methods, each with its own advantages and challenges. Masterbatch coloring, liquid coloring, dry blending, and co-extrusion are some of the techniques used to achieve vibrant and consistent colors in polycarbonate products. Despite the challenges related to color stability, pigment compatibility, and processing conditions, the benefits of colored polycarbonate, including enhanced aesthetic appeal, functional enhancements, and increased marketability, make it a valuable material in numerous industries.
For more information about adding color to polycarbonate, you can contact me at simon@chiancess.com.
References:
1. American Plastics Council. (2020). Polycarbonate (PC) Plastic: Properties, Uses, & Structure. Retrieved from https://www.americanplasticscouncil.org.
2. Kuo, M. (2021). Polycarbonate: A Versatile, Strong Plastic. Retrieved from https://www.thoughtco.com.
3. Saeed, S. M., & Abd-El-Barr, M. M. (2020). Polycarbonate Sheets: A Comparative Review. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 28(3), 685-699.
4. Ligon, S. C., & Liska, R. (2021). Polycarbonate and Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) Photopolymerizable Materials for Additive Manufacturing. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 3(4), 1257-1269.
5. Foy, M. (2020). The Benefits of Using Polycarbonate. Retrieved from https://www.architectureanddesign.com.au.
6. Jain, S. K. (2021). Polycarbonate Sheets: Properties and Applications. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 34(12), 1673-1694.
.webp)