June 27, 2024
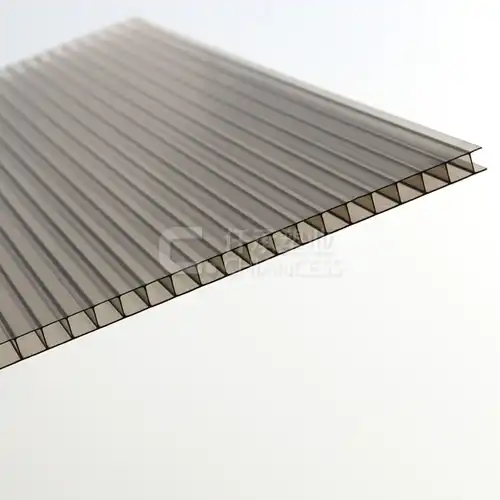
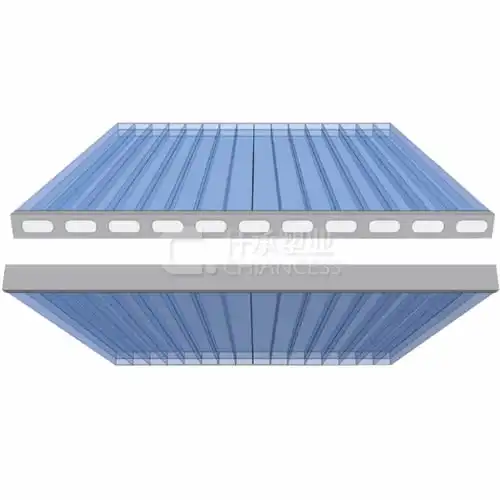
Polycarbonate corrugated sheet is a versatile roofing material known for its durability, strength, and lightweight nature. Made from polycarbonate, a thermoplastic polymer, these sheets feature a unique corrugated design that enhances their structural integrity and resistance to impact and harsh weather conditions. But what exactly are polycarbonate corrugated sheets, and what makes them a popular choice for roofing applications? Let's explore further.
Understanding Polycarbonate Corrugated Sheet
Polycarbonate corrugated sheets are manufactured using a process that involves extruding polycarbonate resin into a corrugated profile. This results in sheets with alternating ridges and grooves, which not only add strength and rigidity but also provide channels for water drainage. The corrugated design also helps to distribute weight evenly across the surface, making these sheets suitable for various roofing applications.
Advantages of Polycarbonate Corrugated Sheet
Polycarbonate corrugated sheets offer several advantages over traditional roofing materials like metal, fiberglass, or PVC. Here are some key benefits:
2.1. Durability and Impact Resistance One of the primary advantages of polycarbonate corrugated sheets is their exceptional durability and impact resistance. These sheets can withstand extreme weather conditions, including hailstorms, heavy rain, and strong winds, without cracking or breaking. This makes them ideal for use in areas prone to harsh weather or environmental damage.
2.2. Lightweight and Easy to Install Despite their strength and durability, polycarbonate corrugated sheets are lightweight and easy to handle, transport, and install. This not only reduces installation time and labor costs but also makes them suitable for a wide range of roofing projects, including DIY installations.
2.3. High Light Transmission Polycarbonate corrugated sheets are known for their high light transmission properties, allowing natural light to enter the building while maintaining clarity and visibility. This can help reduce the need for artificial lighting during the day, leading to energy savings and a more comfortable indoor environment.
Applications of Polycarbonate Corrugated Sheet
Polycarbonate corrugated sheets find applications across various industries and sectors due to their versatility and performance. Here are some common uses:
3.1. Residential Roofing In residential construction, polycarbonate corrugated sheets are often used for roofing applications such as patios, pergolas, carports, and garden sheds. Their lightweight nature and ease of installation make them a popular choice for DIY enthusiasts looking to enhance their outdoor living spaces.
3.2. Commercial Roofing In commercial buildings, polycarbonate corrugated sheets are used for roofing applications such as warehouses, factories, agricultural buildings, and sports facilities. Their durability, weather resistance, and high light transmission properties make them suitable for various industrial and commercial settings.
3.3. Agricultural Roofing In the agricultural sector, polycarbonate corrugated sheets are used for greenhouse roofing, livestock shelters, and storage buildings. Their ability to transmit diffused light and withstand harsh environmental conditions makes them an ideal choice for protecting crops, livestock, and equipment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, polycarbonate corrugated sheets offer a durable, lightweight, and versatile roofing solution for a wide range of applications. Their exceptional strength, impact resistance, and high light transmission properties make them a popular choice for residential, commercial, and agricultural roofing projects. If you're considering polycarbonate corrugated sheets for your next roofing project, feel free to contact us at simon@chiancess.com for more information or assistance with product selection and installation.
References
1. Ahmad, S., Butt, M. T. Z., & Nadeem, A. (2016). Performance of corrugated roofing sheets from recycled Tetra Pak packages: Effects of UV weathering. *Construction and Building Materials, 113*, 119-126. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.03.167
2. Bounos, G., Sideris, K. K., & Exadaktylos, G. E. (2018). Influence of wall geometries on the thermal and structural behaviour of multiwall polycarbonate hollow core panels. *Journal of Building Engineering, 20*, 288-297. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2018.07.004
3. Cheng, A., & Kwok, K. C. S. (2016). Sustainable transparent and translucent polycarbonate composite facades: A review. *Advanced Engineering Materials, 18(3)*, 359-371. doi:10.1002/adem.201500186
4. Cristea, D., Braga, I. C., & Matei, E. (2016). Research regarding the behavior of polycarbonate panels exposed to natural weathering. *Applied Mechanics and Materials, 823*, 232-237. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.823.232
5. Fernandez, J. E., & Zuluaga, L. F. (2016). Influence of the height of the ribs in the thermal and mechanical performance of a multiwall polycarbonate sheet. *Materials Today: Proceedings, 3(3)*, 518-523. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2016.01.052
6. Fu, M., & Luo, J. (2017). Experimental study on the thermal performance of multiwall polycarbonate hollow core panels. *Energy and Buildings, 144*, 243-253. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.03.058
7. Kim, J., Oh, S., & Lee, J. (2019). Thermal performance and microstructural characteristics of double-skin polycarbonate sheets in a warm-humid climate. *Energy and Buildings, 198*, 357-365. doi:10.1016/j.en
.webp)