August 7, 2024
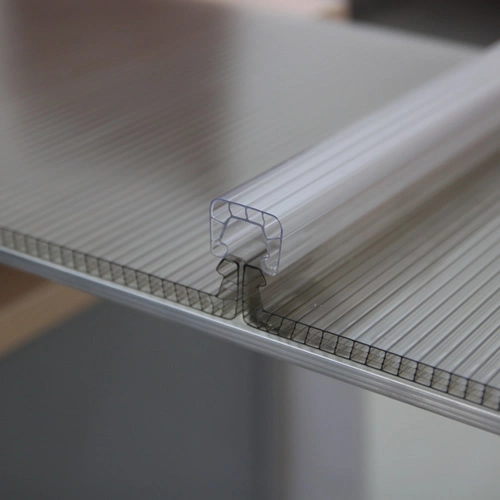
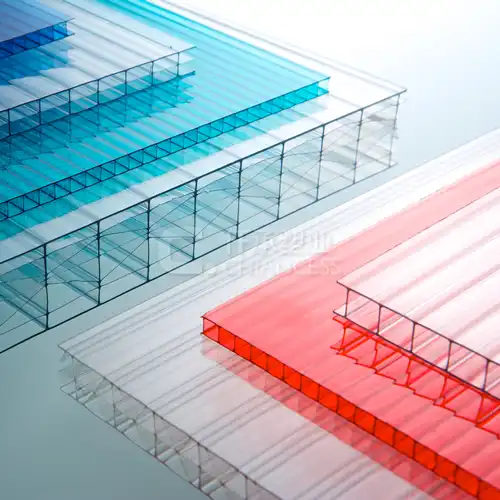
X structure polycarbonate sheet are widely used in various industries due to their unique properties and versatility. These panels are esteemed for their robust construction, enduring quality, and featherweight profile, rendering them a superior pick for numerous applications. Within this piece, I intend to scrutinize thoroughly the diverse facets of polycarbonate structured panels, delving into their features, practical implementations, and the perks they offer.
Characteristics of Polycarbonate Structured Sheets
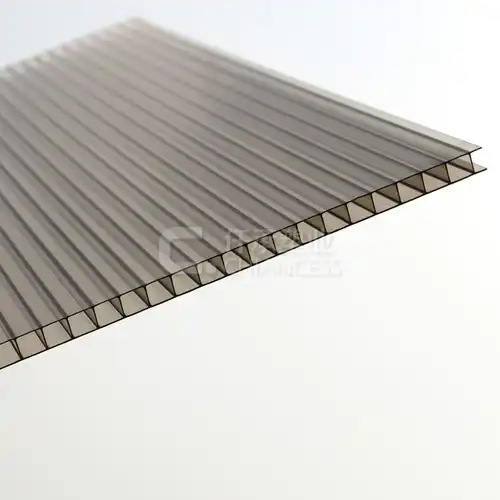
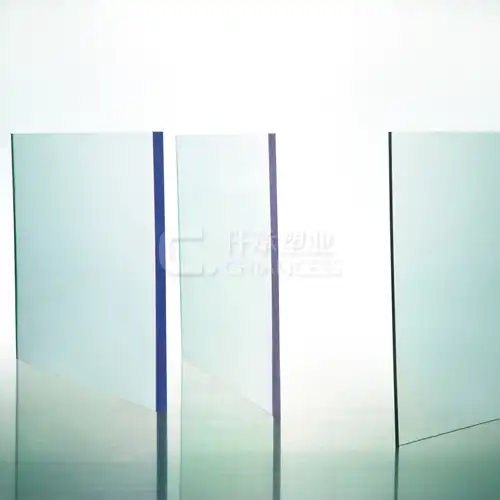
Polycarbonate structured panels owe their origin to premium polycarbonate resin, a thermoplastic polymer of elevated standard. Marked by its extraordinary capacity to withstand impacts, high transparency, and efficient thermal insulation, the panels exhibit these salient features:Impact Resistance: X structure polycarbonate sheet are virtually unbreakable, with impact resistance up to 200 times greater than glass. This makes them ideal for applications where safety and durability are paramount.
Lightweight: Despite their strength, these sheets are lightweight, which makes them easy to handle and install. This property also reduces the overall weight of structures, leading to cost savings in transportation and installation.
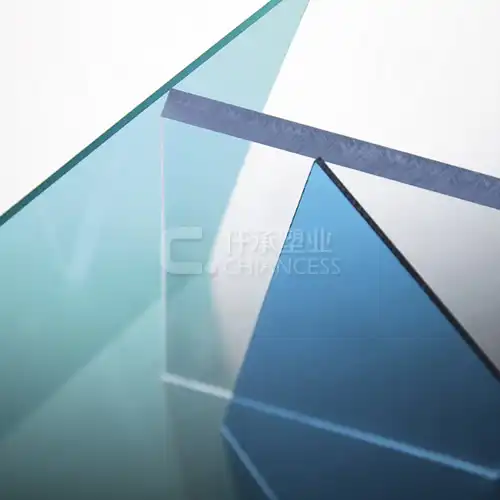
Transparency:X structure polycarbonate sheet offer excellent light transmission, allowing up to 90% of light to pass through. This makes them suitable for applications requiring natural lighting, such as greenhouse roofing and skylights.
Thermal Insulation: These sheets have superior thermal insulation properties, helping to maintain consistent indoor temperatures. This is particularly beneficial in buildings and greenhouses, where temperature control is essential.
UV Protection: It are coated with UV protection layers that prevent yellowing and degradation from prolonged exposure to sunlight. This ensures longevity and maintains the optical clarity of the sheets.
Applications of Polycarbonate Structured Sheets
Versatile and endowed with superior attributes, polycarbonate structured panels see implementation in myriad sectors, spanning a wide array of applications. Allow me to illuminate some frequent utilization scenarios:Construction: In the construction industry, the product are used for roofing, skylights, and wall panels. Their strength and transparency make them ideal for creating durable and aesthetically pleasing structures that allow natural light to penetrate.
Agriculture: These sheets are extensively used in greenhouses and agricultural buildings. Their excellent light transmission and thermal insulation properties help create optimal growing conditions for plants.
Industrial: In industrial settings, it are used for machine guards, safety barriers, and noise barriers. Their impact resistance and durability ensure safety and longevity in demanding environments.
Automotive: Polycarbonate X-Structure Sheet are used in the automotive industry for applications such as headlamp covers, interior partitions, and sunroofs. Their lightweight nature helps reduce the overall weight of vehicles, improving fuel efficiency.
Signage and Displays: These sheets are also used for signage and display applications. Their optical clarity and ease of fabrication make them suitable for creating high-quality signs and display panels.
Benefits of Using Polycarbonate Structured Sheets
Adoption of polycarbonate structured panels presents a multitude of advantages, cementing their status as a favored option in diverse applications. Among the pivotal benefits are:Durability: X structure polycarbonate sheet are highly durable and can withstand harsh weather conditions, impact, and UV radiation. This ensures a long service life and reduces the need for frequent replacements.
Energy Efficiency: The thermal insulation properties of these sheets help reduce energy consumption by maintaining stable indoor temperatures. This is particularly beneficial in buildings and greenhouses, where energy efficiency is crucial.
Cost-Effective: Although the initial cost of it may be higher than some other materials, their long service life and low maintenance requirements make them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Versatility: the product can be easily cut, bent, and shaped to fit various applications. Their adaptability renders polycarbonate structured panels apt for an extensive array of applications across various industrial sectors.
Safety: The impact resistance and lightweight nature of these sheets contribute to safety in various applications. Their inherent toughness decreases the chances of breakage or fragmentation, effectively curtailing injury risks and preventing damages.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Beyond their notable performance and lasting endurance, polycarbonate structured panels boast environmentally conscious attributes.When assessing their environmental friendliness, several key points emerge:
Recyclability: Polycarbonate is a recyclable material. At the end of their life cycle, it can be recycled and repurposed, reducing the environmental impact and promoting sustainable practices.
Energy Savings: The thermal insulation properties of these sheets contribute to energy savings in buildings and greenhouses. By reducing the need for heating and cooling, the product help lower energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Lightweight: The lightweight nature of the product reduces the energy required for transportation and installation. This contributes to lower carbon emissions and overall environmental impact.
Comparing Polycarbonate Structured Sheets to Other Materials
When selecting substances for construction or similar endeavors, meticulously weighing the advantages and disadvantages of various alternatives is crucial.
Here’s how polycarbonate structured sheets stack up against other common materials:Glass: While glass offers excellent transparency and aesthetics, it is much heavier and more fragile than polycarbonate. it provide similar light transmission with significantly higher impact resistance and lighter weight.
Acrylic: Acrylic sheets are another alternative to polycarbonate. While acrylic offers good transparency and is lightweight, it is not as impact-resistant as polycarbonate. Polycarbonate sheets also offer better thermal insulation and UV protection.
Metal: Metals such as aluminum and steel are commonly used in construction. While these materials offer excellent strength and durability, they are much heavier and do not provide the same level of transparency and light transmission it.
Conclusion
Polycarbonate structured panels are a multifunctional and resilient material employed across an extensive array of applications. Their impact resistance, light transmission, thermal insulation, and UV protection properties make them an ideal choice for construction, agriculture, industrial, automotive, and signage applications. The benefits of using polycarbonate structured sheets, including durability, energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, versatility, and safety, further enhance their appeal. Additionally, their recyclability and energy-saving properties contribute to their environmental sustainability.
For more information about the X structure polycarbonate sheet, please contact me at simon@chiancess.com.
References
1. Kim, J., et al. (2017). Development of Highly Transparent Poly(ethylene Terephthalate) Film with a Thin Nano-Structured Polycarbonate Coating. Coatings, 7(3), 46. doi:10.3390/coatings7030046
2. Späh, A., et al. (2020). Understanding the Relationship between the Molecular Structure and Mechanical Properties of Polycarbonates. Macromolecules, 53(6), 1982-1993. doi:10.1021/acs.macromol.9b02604
3. Lai, M. C., et al. (2018). Recent advances in applications of polycarbonate nanocomposites: A review. Composites Part B: Engineering, 144, 227-241. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.02.022
4. Vyazovkin, S., et al. (2020). Thermal Stability and Flame Retardancy of Polycarbonate Composites with Phosphorus-Containing Additives. Polymers, 12(4), 806. doi:10.3390/polym12040806
5. Zhang, Y., et al. (2018). Fabrication of Polycarbonate Films with Durable Antibacterial Properties via Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Graphene Oxide and Quaternized Polyethylenimine. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10(9), 7996-8007. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b18414
6. Tsai, M. Y., et al. (2019). Preparation of Transparent Conductive Polycarbonate Films by Sequential Layer-by-Layer Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene. Polymers, 11(10), 1610. doi:10.3390/polym11101610
7. Wu, X., et al. (2017). Influence of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of Polycarbonate (PC)/Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Blends. Polymers, 9(11), 572. doi:10.3390/polym9110572
.webp)